
How to Invest in Multi-Touch Attribution: A Practical Guide
Author:
Neha Bhuchar
Last Updated:
Feb 19, 2026
Published on:

Table of Contents
Today’s customer journey is rarely a straight line. Shoppers often see a social post, click a search ad, and read an email before they finally decide to buy. Multi-touch attribution is simply a method of giving credit to every step in that journey, rather than just thanking the final click. Unlike older models that only look at the last interaction, this approach recognizes that it takes a combination of different channels and touchpoints working together to drive a sale.
Understanding this concept is vital because it reveals the true performance of your marketing. Instead of viewing channels in isolation, it helps you see how they support one another to move a customer down the funnel. This clarity allows you to allocate your budget more effectively, doubling down on the high-value combinations that actually drive revenue while eliminating the blind spots that come from looking at only one touchpoint.
This guide covers the essentials of how it works, the different models available, and the tools you need to get started.
How Does Multi-Touch Attribution Work?
At its core, multi-touch attribution connects the dots of a user’s digital footprint. By using tracking technologies like cookies, pixel tags, and CRM data, the system records every ad click, site visit, and email open. All this data flows into a central platform that stitches these scattered interactions into a single, cohesive story for each customer. The most critical requirement here is a unified analytics hub; without it, you are left with isolated data points that fail to show the full picture of the user experience.
What Are the Types of Multi-Touch Attribution Models?
Once the data is collected, your chosen MTA model decides how much "credit" each step deserves. The infographic below explains how each model works.
Here’s what each model offers:
The Linear Model gives equal importance to all touchpoints, useful for new businesses.
A Time-Decay model gives more weight to the most recent interactions, making it great for long sales cycles where the final push matters most.
A U-Shaped model emphasizes the very first discovery and the final conversion.
W-Shaped models are used by B2B companies to track key milestones throughout a complex funnel.
Custom attribution models using machine learning can provide accurate insights but require significant data volume and technical expertise.
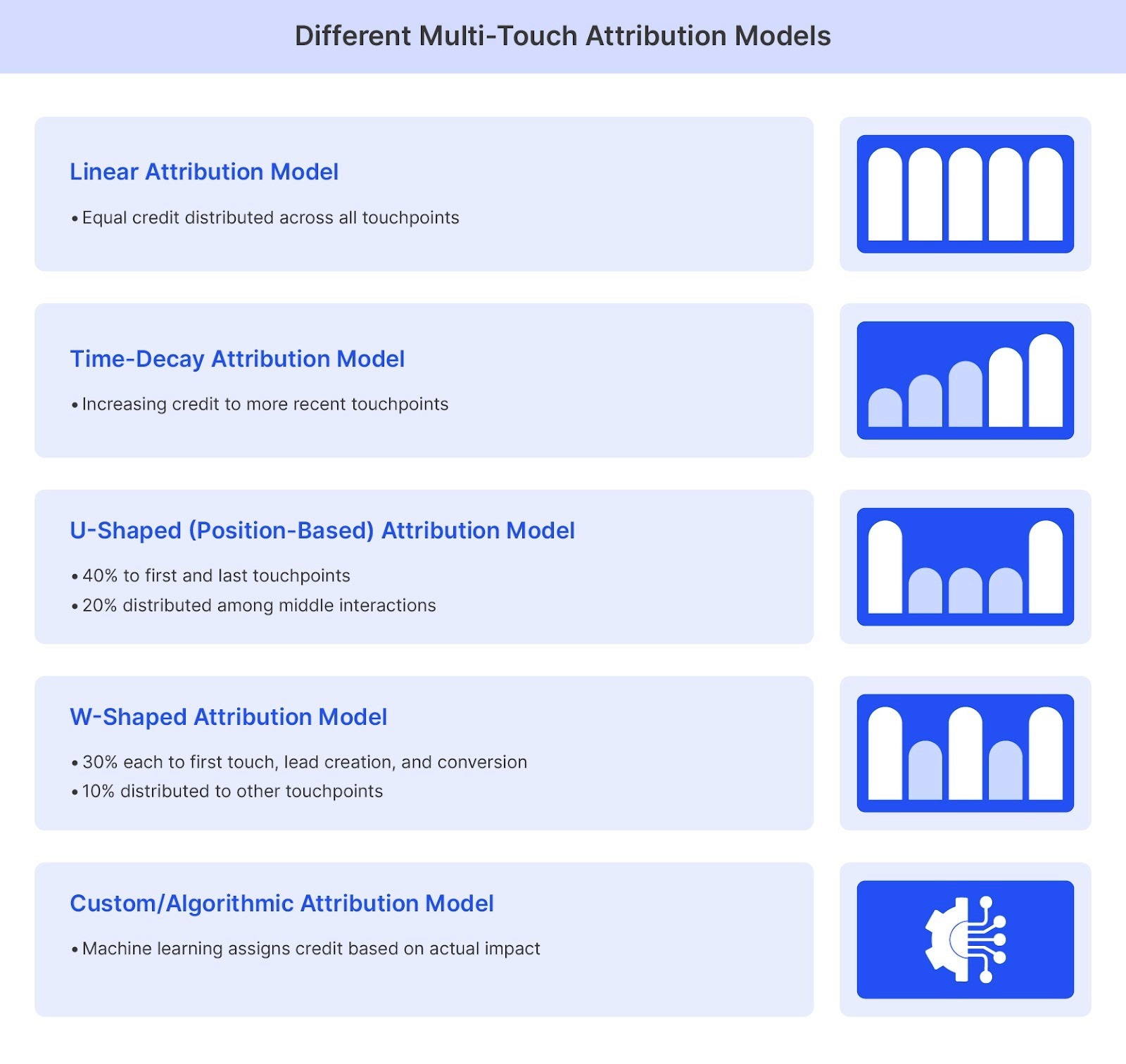
The best approach is to start with a model that matches your sales cycle's length and complexity, eventually evolving toward advanced, algorithmic methods as your data capabilities grow.
| Related read: Amazon Data Analysis: Tools, Metrics & Best Practices
Is Multi-Touch Attribution Better than Single-Touch Attribution?
For most modern businesses, multi-touch attribution is indeed better than single-touch attribution. This is because it accurately shows how different marketing channels work together to make a sale. While single-touch might work for simple, instant purchases, it misses the real customer journey, like when someone clicks an ad, checks social media, and reads an email before buying. If you invest in multiple channels, multi-touch gives you the full picture you need to spend your budget wisely and get better results.
Differences between Multi-Touch Attribution and Single-Touch Attribution
Factor | Multi-Touch Attribution | Single-Touch Attribution |
Customer Journey | Offers an accurate view of the journey across multiple touchpoints. | Best for very short sales cycles with minimal interactions. |
Channel Scope | Ideal for businesses managing multiple marketing efforts simultaneously. | Sufficient for strategies using only one or two primary channels. |
Budget & Insights | Enables better budget allocation by revealing how campaigns work together (synergies). | Suitable for direct response campaigns where the last click clearly drives the result. |
Business Complexity | Supports full-funnel optimization from awareness to conversion. | Practical for small businesses with simple journeys or resource constraints. |
How Does Multi-Touch Attribution Improve ROI Measurement?
Multi-touch attribution transforms how you measure marketing effectiveness by showing true channel contribution rather than last-click bias.
Eliminates Last-Click Bias: Accurately assigns credit to every impactful touchpoint instead of just the final interaction.
Optimizes Budget Allocation: Shifts spend toward channels that drive value across the entire funnel, preventing over-investment in bottom-funnel tactics.
Uncovers Winning Sequences: Identifies specific combinations of channels (e.g., social ads followed by email) that convert best.
Validates Top-of-Funnel Impact: Prevents the mistake of cutting awareness campaigns that assist conversions without driving immediate sales.
Refines Campaign Strategy: Enables holistic testing to see how changes in one channel affect the entire customer journey.
| Related read: 3 Must-Track Amazon Advertising Metrics Beyond ACoS
What Channels Are Included in Multi-Touch Attribution?
Multi-touch attribution can track virtually every interaction a customer has with your brand, both online and offline. It primarily covers digital channels like paid search, social media, email, and video ads, which offer the most precise data. However, it also includes e-commerce activities like retargeting and marketplace ads, and can even account for offline efforts (TV, radio, direct mail, etc.) by using tracking promo codes or surveys to link them to final sales.
Channel | Examples | Characteristic |
Digital Channels |
| The Foundation: Provides the most trackable data and offers the easiest integration with attribution tools. |
E-commerce & Retail |
| Sales-Focused: Critical for online sellers, though platforms like Amazon often require specialized tracking approaches. |
Offline Channels |
| Advanced Implementation: Harder to track; connected to digital data via promo codes, surveys, or matched market testing. |
Pro tip: The number of channels you track depends on your marketing strategy and technical infrastructure. Focus first on primary digital marketing channels where tracking is most reliable, then expand over time as your data collection ability matures.
What Tools Are Used for Multi-Touch Attribution?
The attribution tools landscape includes enterprise platforms, specialized solutions, and custom builds.
Enterprise Attribution Platforms: These offer comprehensive tracking and machine learning capabilities suitable for complex organizational needs. Examples: Google Analytics 4, Adobe Analytics.
Specialized Attribution Solutions: Dedicated tools that focus specifically on attribution challenges to provide deeper insights than general analytics platforms. Examples: Ruler Analytics, Hyros.
Amazon-Specific Tools: Solutions designed to track cross-channel performance and connect off-Amazon traffic to Amazon conversions. Example: Amazon Marketing Cloud (AMC)
Pro Tip: Certain Amazon PPC software, such as atom11, leverage AMC to layer retail signals (inventory levels, Buy Box status, competition, and more) directly onto the attribution path. This allows advertisers to distinguish between conversions driven by marketing influence versus those resulting from operational availability.
Marketing Analytics Platforms: Flexible business intelligence tools that allow you to build custom attribution reporting on top of your existing infrastructure. Examples: Looker, Tableau.
Custom Solutions: Proprietary models built by in-house data science teams using code or SQL for maximum flexibility and customization. Examples: Python/R models, SQL-based logic.

Pro tip: When choosing attribution tools, consider your business size and complexity, evaluate technical capabilities and resources, assess budget constraints, and ensure integration with your existing martech stack. Start with native platform tools like Google Analytics 4 before investing in specialized solutions. Most businesses can accomplish meaningful attribution without expensive enterprise software.
How to Implement Multi-Touch Attribution
Successful attribution implementation requires systematic planning and execution.
Step 1: Define Goals and Success Metrics
First, pinpoint the conversion events that drive your business. For online stores, this is usually a purchase; for B2B companies, it might be a demo request or a qualified lead. Decide which stages of the customer journey you need to measure and set your baseline numbers before you start building.
Step 2: Map the Customer Journey
Map out every touchpoint a customer hits, from the moment they find you to the moment they buy. Identify your main channels and interactions to understand the standard path to purchase. This process often highlights gaps in your current tracking and shows you where the customer experience needs improvement.
Step 3: Implement Proper Tracking
Set up consistent UTM parameters for every single marketing campaign. Install conversion pixels from your ad platforms to catch every action. Ensure this data flows into a central analytics hub where you can review it. Test your tracking accuracy by making a purchase yourself; poor data will ruin even the best model.
Step 4: Choose Starting Attribution Model
Start with a simple model, like linear or time-decay instead of jumping straight into complex algorithms. Pick a model that matches your business style and plan to upgrade to smarter methods as you learn more. The best starting model is one that balances accuracy with being easy to understand.
Step 5: Select Attribution Tools
Choose tools that match your current needs and budget. It is often best to start with the built-in features of Google Analytics or your current marketing software. You can always move to specialized, paid tools later as you scale up and your attribution needs become more demanding.
Step 6: Collect, Analyze, and Interpret Data
Connect your marketing platforms and unify customer IDs to link interactions across different channels. Build a scalable data pipeline or warehouse, then compare different models to see which touchpoints matter most. This step turns your raw data into a clear, actionable strategy you can actually use.
Step 7: Adjust Marketing Strategy Based on Insights
Shift your budget toward the high-performing touchpoints found in your analysis. Fix or cut the channels that aren't pulling their weight. Test these changes and measure how they impact your total conversion rates. Attribution is only valuable when you take the insights and turn them into real action.
Step 8: Iterate and Improve
Fix your tracking setup whenever you find gaps in the data. Test different attribution models to double-check your findings. Expand your tracking to new channels as your team gets better at this. Attribution isn't a one-time project; it is an ongoing process of learning, testing, and optimizing.
What Are the Challenges of Multi-Touch Attribution?
Data Collection and Integration Complexity: Unifying data across platforms and devices is difficult due to privacy regulations and technical gaps. This often breaks the connection between online and offline customer interactions.
Technical Implementation Requirements: Setup demands robust data warehousing and deep integration across marketing tools. Most marketing teams will need to rely on IT or data engineers, which can slow down the process.
Attribution Window Decisions: Deciding how far back to look involves balancing data comprehensiveness with relevance. You must determine if a 7, 30, or 90-day window best fits your specific sales cycle.
Privacy and Compliance Constraints: Regulations like GDPR and CCPA restrict tracking capabilities, reducing the visibility of user behavior. This forces reliance on modeled data rather than exact history, introducing some uncertainty.
Data Quality and Volume Requirements: Models require a high volume of clean, consistently named data to work effectively. Without regular validation, "garbage-in, garbage-out" errors will undermine confidence in your insights.
Model Selection and Bias: No model is perfect; each carries inherent assumptions about how credit should be distributed. It is best to avoid over-complicated custom models that are difficult to explain to stakeholders.
Organizational Adoption: Gaining buy-in is difficult because teams often resist changes to how their performance is measured and budgeted. Success requires executive support to shift the focus from simple last-click metrics to better decision-making.
These challenges are surmountable with proper planning, appropriate tools, and realistic expectations. Most businesses benefit from starting simple and building attribution capabilities over time rather than attempting a perfect implementation immediately.
Conclusion
Multi-touch attribution provides essential visibility into modern marketing performance, moving beyond the limitations of last-click models. To get started, focus on defining clear goals, establishing proper tracking infrastructure, and selecting a simple attribution model that fits your current needs. As your data volume and technical capabilities grow, you can evolve your approach to include more sophisticated, algorithmic methods. Ultimately, investing in multi-touch attribution enables smarter budget allocation and improved ROI by revealing exactly how your channels work together.
For Amazon-specific advertisers, platforms like atom11 uniquely connect ad performance with retail signals, ensuring you have the complete picture needed to scale effectively. Book a demo to see how atom11 helps Amazon advertisers understand true campaign impact across the entire customer journey.
FAQs
What is multi-touch attribution?
Multi-touch attribution assigns credit to multiple marketing touchpoints throughout the customer journey rather than crediting only a single interaction. It provides accurate insights by tracking all interactions from first awareness to final conversion and distributing credit based on chosen attribution models like linear, time-decay, or algorithmic approaches.
Why is multi-touch attribution important in marketing?
Multi-touch attribution reveals true channel performance and how channels work together synergistically. It enables better budget allocation by showing which marketing touchpoints contribute to conversions, improves understanding of customer journey complexity, and eliminates blind spots from last-touch models. This leads to more effective marketing strategies and improved ROI measurement.
What are the different multi-touch attribution models?
Common models include Linear (equal credit to all touchpoints), Time-Decay (more credit to recent interactions), U-Shaped (emphasizes first and last touch with 40% each), W-Shaped (highlights first touch, lead creation, and conversion with 30% each), and Custom/Algorithmic using machine learning. The best attribution model depends on your business type, sales cycle, and available conversion data.
What channels are included in multi-touch attribution?
Multi-touch attribution can include paid search, social media advertising, display advertising, email marketing, organic search, content marketing, affiliate marketing, and even offline channels like TV, print, and events. The specific channels depend on your marketing mix and tracking capabilities. Start with digital channels where accurate data collection is easiest.
How does multi-touch attribution improve ROI measurement?
Multi-touch attribution shows true channel contribution rather than last-click bias, preventing over-investment in bottom-funnel tactics only. It reveals undervalued channels that assist conversions, identifies high-performing touchpoint combinations, and enables optimization of the entire customer experience rather than isolated tactics. This comprehensive view supports more effective budget allocation across your marketing efforts.
What are the challenges of multi-touch attribution?
Key challenges include data collection complexity, technical implementation requirements, privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA reducing tracking capabilities, cross-device tracking difficulties, requiring sufficient data volume for statistical significance, attribution window decisions, and organizational adoption. Most challenges can be overcome with proper planning and appropriate attribution tools.
What tools are used for multi-touch attribution?
Common tools include Google Analytics 4 with data-driven attribution, Adobe Analytics, HubSpot, specialized platforms like Ruler Analytics and Northbeam, and Amazon Marketing Cloud for Amazon attribution. For Amazon advertisers, atom11 integrates retail signals with advertising data for comprehensive insights. Start with native platform tools before investing in specialized solutions.
How is multi-touch attribution different from last-click attribution?
Last-click attribution credits only the final touchpoint before conversion, while multi-touch attribution credits multiple interactions throughout the journey. Multi-touch provides a fuller picture of channel contribution, balances credit across funnel stages, and values top and middle-funnel marketing appropriately.
How do I implement multi-touch attribution?
Start by defining conversion goals and mapping your customer journey. Implement proper tracking with UTM parameters and conversion pixels. Choose a starting point attribution model that matches your business. Select appropriate tools and integrate data sources into a unified platform. Analyze results regularly and adjust your marketing strategy based on insights. Iterate and improve continuously.
How does multi-touch attribution work for Amazon advertising?
Amazon attribution requires connecting paid advertising campaign performance with retail signals like organic rank changes, pricing competitiveness, and Buy Box status. Tools like Amazon Marketing Cloud provide cross-channel insights across Sponsored Products, Sponsored Brands, and Sponsored Display. atom11 specializes in this retail-aware attribution for Amazon, tracking both direct advertising conversions and indirect impacts on organic sales to measure total marketing effectiveness.

